

As a venture capitalist who has traversed the path of a start-up founder and product manager, I am excited to share some insights on Venture Design, a pivotal framework for your success.
Setting: Changing Goals Throughout the Start-up Journey
In the world of Venture Design, the needs of a start-up and the milestones they must meet evolve with every stage of the fundraising journey. Let's dive into the critical outputs for each stage, all while incorporating product management and venture-building best practices - building the right product and building the product right.
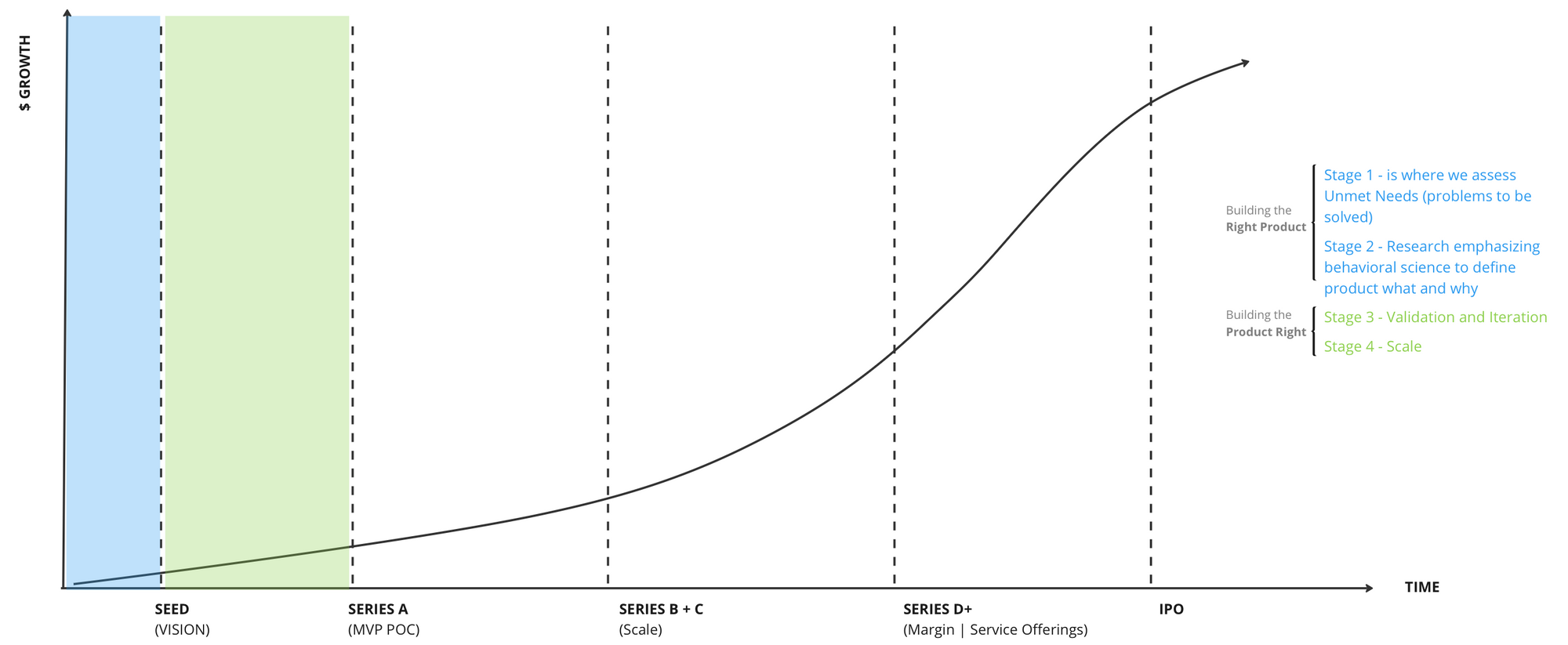
- Seed Stage: At the beginning of your journey, the primary goal is to validate your idea and build a strong foundation. Outputs to focus on include a well-defined problem-solution fit, early prototypes, and proof of concept to attract initial investors.
- Early-Stage: As you gain traction, the focus shifts to achieving product-market fit. Outputs at this stage include a refined MVP (Minimum Viable Product), user feedback, and initial customer acquisition strategies.
- Growth Stage: With validation in hand, it's time to scale. The outputs to concentrate on include expanding your customer base, optimizing user experience, and setting scalable processes for customer support and sales.
- Expansion Stage: As you continue to grow, the goal now is to enter new markets or explore product extensions. Outputs to consider include market research, localization strategies, and diversifying your offerings to cater to different customer segments.
- Late-Stage: Congratulations! You've reached a significant milestone. At this stage, your focus should be on maximizing profitability and preparing for potential exits or further fundraising. Outputs include financial stability, expansion plans, and strategies for potential mergers or acquisitions.
Throughout this journey, never lose sight of the core principles of product management - building the right product that fulfills genuine market needs and building the product right with a relentless focus on quality and user experience.
I encourage you to embrace the iterative mindset, be adaptable to market feedback, and stay true to your vision. Surround yourself with a passionate team that shares your values, and remember that the most successful ventures are born from perseverance and learning from both successes and failures.
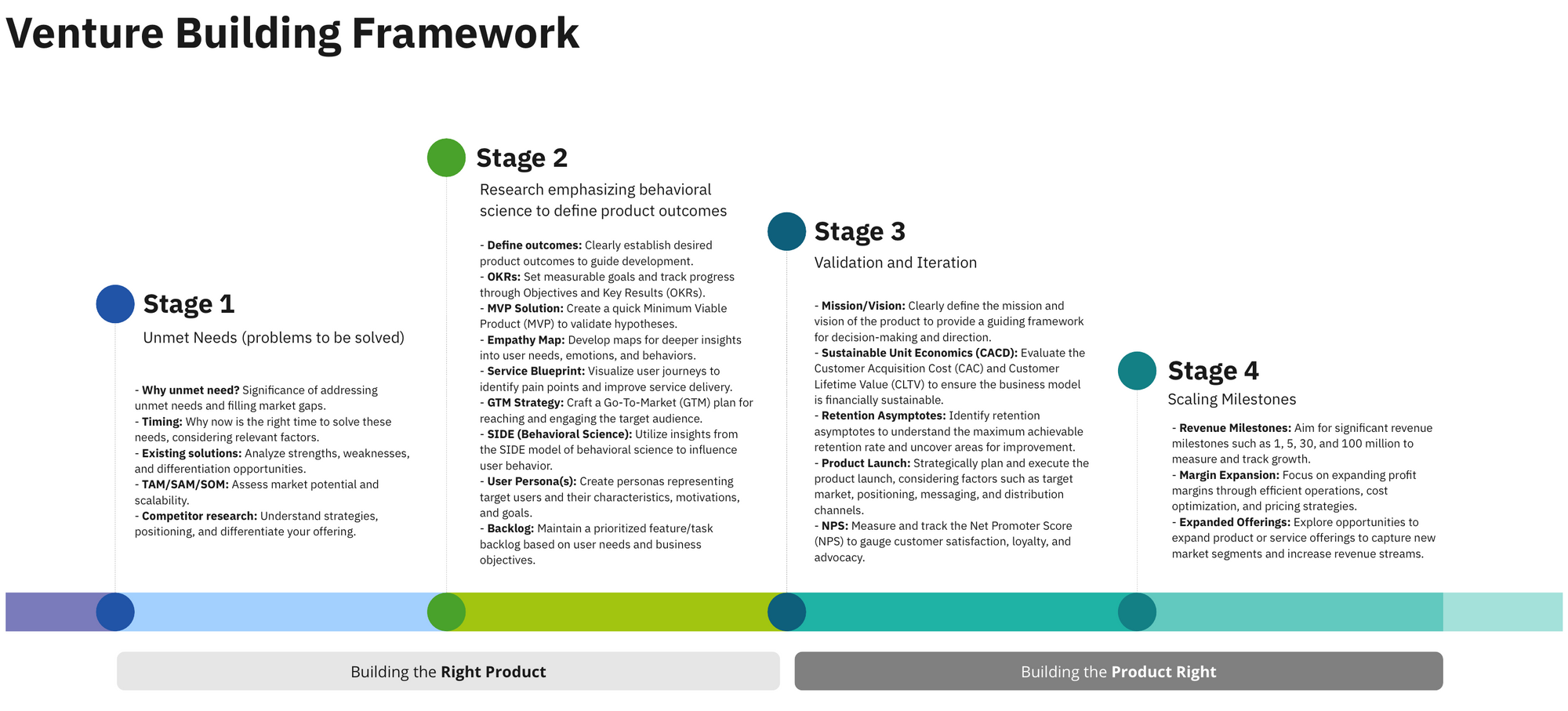
Stage 1: Unlocking Opportunities Through Unmet Needs
At the heart of any entrepreneurial endeavor lies the identification and resolution of unmet needs. These unaddressed problems, when uncovered and tackled, serve as the bedrock for disruptive innovation. But why focus on unmet needs specifically?
Unmet needs hold immense potential because they represent gaps in the market where existing solutions fail to fully satisfy customer requirements. By zeroing in on these gaps, you have the opportunity to create something truly valuable and capture a significant share of the market. Unmet needs often serve as catalysts for revolutionary products or services that transform industries, fostering growth and attracting investor interest.
Timing is crucial when it comes to solving unmet needs. While an unmet need may exist for years, it is the convergence of several factors that makes now the opportune moment to address it. Technological advancements, shifts in consumer behavior, regulatory changes, or emerging market trends can all contribute to the perfect storm of conditions that allow a solution to thrive. Understanding the current landscape and recognizing these enabling factors is key to capitalizing on the present moment.
Before diving headfirst into solving an unmet need, it is important to explore existing solutions. This step helps you gain valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of potential competitors. By analyzing their offerings, you can identify areas where your solution can differentiate itself and deliver unique value to customers. Additionally, studying the existing solutions allows you to learn from their successes and failures, enabling you to refine your approach and build upon existing knowledge.
When evaluating the market potential for your solution, it's important to consider the Total Addressable Market (TAM), Serviceable Addressable Market (SAM), and Serviceable Obtainable Market (SOM). The TAM represents the total demand for a particular product or service, while the SAM refers to the portion of the TAM that you can realistically target. The SOM further narrows down the SAM to reflect the share of the market you can effectively capture given your resources, competition, and go-to-market strategy. Understanding these market dimensions helps you gauge the scalability and viability of your venture.
Competitor research is a critical aspect of Venture Design. It allows you to identify and assess both direct and indirect competitors who are attempting to solve the same unmet need. By thoroughly analyzing their strengths, weaknesses, market positioning, and customer feedback, you gain invaluable insights that inform your own strategy. Competitor research empowers you to differentiate your offering, create a compelling value proposition, and identify unique selling points that set your venture apart from the crowd.
As you embark on your entrepreneurial journey, I encourage you to embrace the process of Venture Design. By carefully understanding unmet needs, recognizing the opportune moment, studying existing solutions, evaluating market potential, and conducting comprehensive competitor research, you lay a solid foundation for success. Remember to leverage your intellectual curiosity, adaptability, and perseverance to navigate the dynamic landscape of entrepreneurship.
Stage 2: Behavioral Science Research to Define Product Outcomes
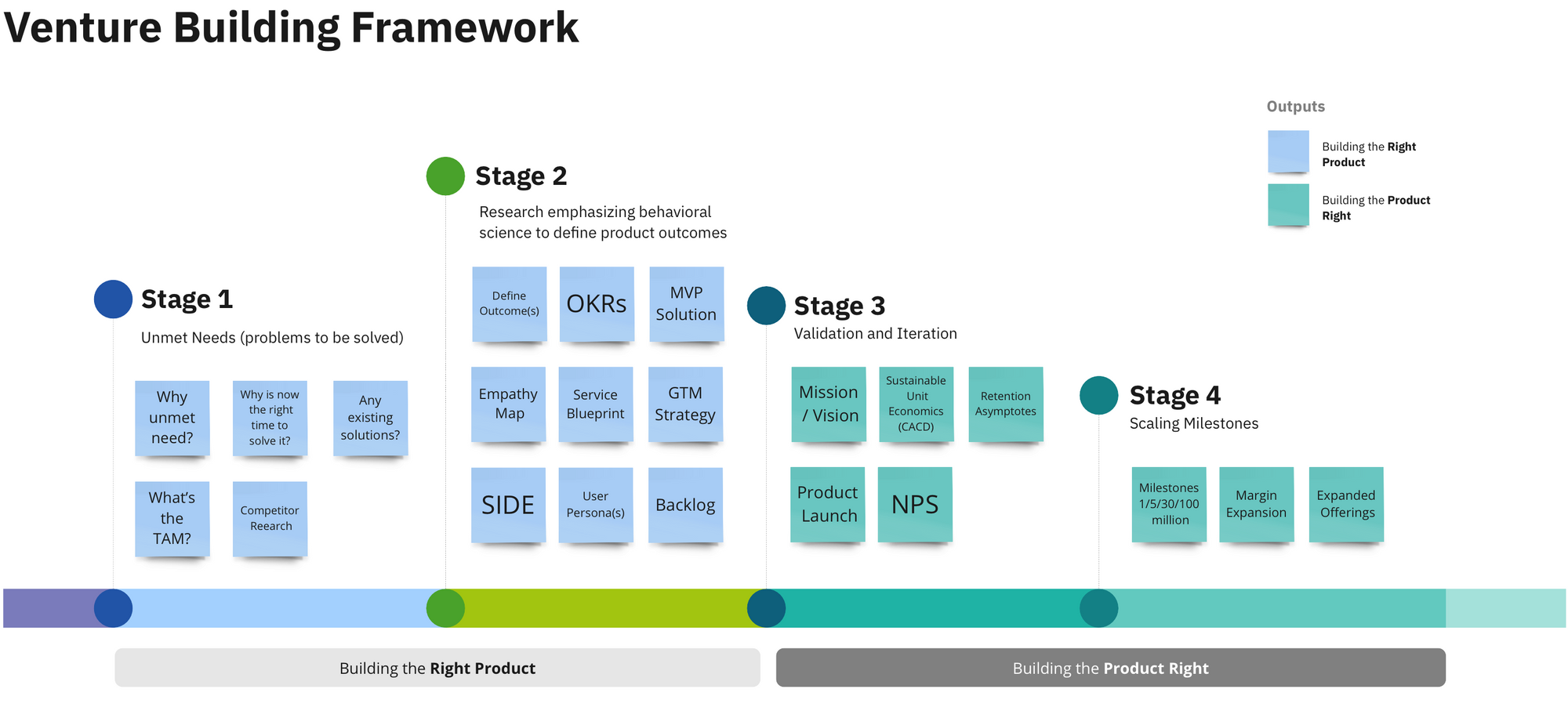
- Define Outcome(s): One of the critical steps in Venture Design is to clearly define your desired product outcomes. By setting a clear vision for what you want to achieve, you create a guiding light that steers the entire development process.
- OKRs (Objectives and Key Results): Setting up Objectives and Key Results is a powerful way to establish measurable goals and systematically track your progress. These OKRs act as milestones, keeping your team focused and aligned as you work towards your larger vision.
- MVP Solution (Minimum Viable Product): In a fast-paced and dynamic startup environment, developing a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) can be a game-changer. It enables you to quickly test and validate hypotheses, allowing for early feedback from users that informs further development.
- Empathy Map: Understanding your users on a deeper level is vital. Developing empathy maps helps you gain insights into their needs, emotions, and behaviors. This valuable information serves as a compass in designing products that truly resonate with your target audience.
- Service Blueprint: To deliver exceptional user experiences, you need to visualize the entire user journey and the underlying service delivery process. A service blueprint helps you identify pain points and areas for improvement, resulting in a more holistic and user-centric approach.
- GTM Strategy (Go-To-Market): An impeccable product requires an equally strong go-to-market strategy. Crafting a well-thought-out GTM strategy outlines how you'll reach and engage your target audience, creating a winning formula for successful product adoption.
- SIDE (Behavioral Science): Behavioral science plays a pivotal role in understanding how users think, feel, and act. Leveraging insights from the Strategy, Insight, Design, Evaluate (SIDE) model can help you nudge user behavior in ways that drive positive outcomes.
- User Persona(s): To make your product more relatable and appealing, create user personas that represent your target audience's characteristics, motivations, and goals. This humanizes your target market and informs your design decisions.
- Backlog: As you dive into product development, maintaining a well-prioritized backlog of features and tasks based on user needs and business objectives ensures that your efforts remain focused and aligned.
Venture Design is a process that marries creativity with strategy and empathizes with the needs of the users. Embrace these research-oriented principles, and they will serve as a solid foundation for your journey toward building meaningful, innovative, and successful products.
Stage 3: Validation and Iteration
Focus on refining your vision and strategy through careful validation and continuous improvement.
- Mission/Vision: Revisit and refine your mission and vision statements. These guiding principles are the compass that will keep your team aligned and driven towards achieving a shared purpose.
- Sustainable Unit Economics (CACD): Understanding your unit economics is vital for long-term success. Evaluate your Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) and Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) to ensure your business model is sustainable and economically sound.
- Retention Asymptotes: In the pursuit of growth, retention holds the key to sustained success. Identify retention asymptotes - points where user retention levels plateau - to uncover areas for improvement and foster lasting customer relationships.
- Product Launch: A well-executed product launch can make all the difference. Strategically plan and execute your launch, considering factors like target market, positioning, messaging, and distribution channels to create a powerful impact.
- NPS (Net Promoter Score): Your customers' satisfaction and loyalty are paramount. Continuously measure and track your Net Promoter Score (NPS) to gauge customer sentiment and identify opportunities for enhancement.
Embrace the spirit of validation and iteration as you fine-tune your venture. This stage is an opportunity to optimize your business model, polish your product, and strengthen your connection with your customers. The journey may be challenging, but the rewards of perseverance and adaptability are immeasurable.
Stage 4: Scaling Milestones
- Milestones 1/5/30/100 Million in revenue: Setting revenue milestones is an excellent way to track your progress and growth. Aim high, starting with the goal of reaching the first million, then five, thirty, and eventually one hundred million. These milestones will be significant markers of your venture's success.
- Margin Expansion: Scaling your venture also involves expanding your profit margins. This means optimizing your business operations, controlling costs, and implementing smart pricing strategies. Margin expansion ensures the financial health and sustainability of your venture as it grows.
- Expanded Offerings: To achieve sustainable growth, consider diversifying your product or service offerings. Expanding into new markets or introducing complementary products can open up fresh revenue streams and broaden your customer base.
Remember that scaling requires careful planning and execution. It's a journey of calculated risks, and as a founder, you need to strike a balance between ambition and prudence. Take the time to analyze your market, engage with customers, and continuously improve your offerings.
Output Overlay
Coming Up Next
We will be covering individual Outputs (see above) in subsequent posts. The intent is to first provide a macro-view of the Venture Building framework (the forest) and then delve deeper into subject areas (the individual trees) thereafter.
By doing this, you will be able to know not only what's being discussed, but when and why it's relevant along the start-up journey.
As always, each post will also contain relevant artifacts, assets, templates, frameworks, and resources to help guide you.